



|
Outline of the International Competition
1) Competition sponsor
JTC Corporation (Singapore government organization)
2) Competition theme
The 123,000 sqm building, internally referred to as ‘Techpolis’, will be the first major development in the Central Xchange ? the cluster for the Infocommunications & Media (ICM) industries in one-north. It will be home to ICM research institutes, industry players and supporting industries.
3) Explanation of the awarded project and future schedule
Construction tenders for Technopolis are expected by mid 2002 and groundbreaking will take place in September this year, where the design of the facility is expected to be revealed. The facility is expected to be completed by end 2004.
4) Characteristics of the KUROKAWAs Plan
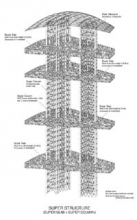
1. Layered City
Eco-Tec City is created by multi-dimensionally layering differing elements (residential, office, public services, commercial). The more layers, the higher the level of vibrancy. A Layered City is created by a new method called Vertical Zoning instead of conventional Horizontal Zoning
2. Vertical Zoning
In principle, residences are placed in the top layer with Roof Garden that is beneficial from the perspective of both the scenic prospect and the privacy it provides. Offices are, in principle, zoned between level 2 and the residential layer. To successfully apply Vertical Zoning, each building is clearly divided into a specialized core for office floors, specialized core for residential floors, and direct elevator to the sky garden and public service floor, and each is provided with its own entrance lobby on the ground floor level. While keeping these vertical zoning systems, it is possible to separately control each tower, with Plot A as RIC + Housing for RIC Researcher, Plot C as ICT + Housing, and Plot B as ICT Annex + Housing.
3. A Super Slab is layered artificial ground.
Eco-Tec City has a layered Super Slab. The urban structure of Eco-Tec City is artificial ground (Super Slab) with multiple layers: the underground is considered to be level zero ground, the surface ground to be level one, the above-ground floors to be levels 2 to Xn, and the roof-top artificial ground level to be level Xr. (Roof Garden).
4. Crack at Level 1 (GL)
Narrow street on the ground surface are cracks (void spaces) of atriums opening to the level zero. Natural light reaches underground level zero through the cracks (void spaces) in the ground. And this crack (void space) is an atrium containing escalators and stairways linking level zero with level one, and it is covered with a roof of transparent glass. The urban underground space that was formerly a black box is now visible from above through this crack (void space). Sidewalks at ground surface level guarantee a width of 4 m on the inside of the building line.
|
|
